What is the treatment for a pimple on the scrotum?
By Claire Sissons
Reviewed by Elaine K. Luo, MD
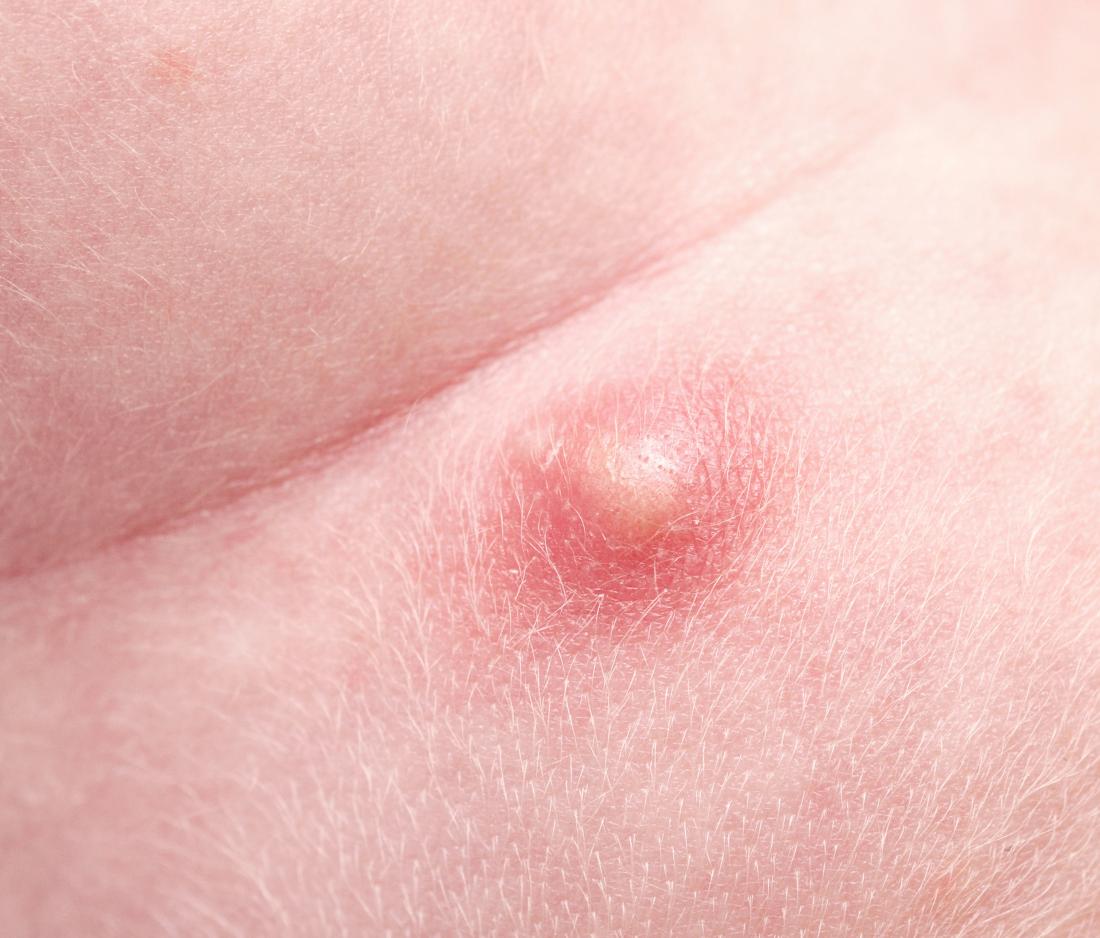
A pimple on the scrotum is usually harmless, but it may also be a sign of a virus or infection. The scrotum can be particularly affected by pimples because sweat and moisture often build up and clog pores in the area.
Sweat and dead skin cells are common causes of pimples. Hence, pimples usually go away without treatment.
The primary cause of pimples is pores that are blocked by:
- dead skin cells
- dirt
- sweat
- natural body oils
When a pore is blocked, bacteria can build up. This causes redness, a raised area of skin, pus, or sometimes all three.
Types and causes
Pimples can form in almost any area of the body, and there are several different types:
- blackheads, which form when oil clogs a pore and the air turns it black
- whiteheads, which form the same way but remain white as the top of the pore is closed
- papules or red bumps that often feel sore when touched
- pustules that have a white tip in their center caused by pus building up
- nodules or bumps below the surface of the skin, which are often painful
Any one of these forms of pimple may develop on the scrotum.
The cause of a pimple on the scrotum is usually the same as for a pimple on the face or back:
Ingrown hair
An ingrown hair is a common cause of a pimple on the scrotum. This happens when a hair twists and grows back into the skin. It usually creates a red spot that can cause itching or discomfort.
An ingrown hair can happen when hair follicles become blocked with dead skin cells. This causes a hair to grow sideways or inward instead of outward. Pubic hair is usually curlier and coarser than the hair on the head, and this type of hair is more likely to become ingrown.
Ingrown hairs are more common on areas that have been shaved. If someone shaves the hair on or around their testicles, this may cause ingrown hairs.
Folliculitis
The hair follicles around an ingrown hair can become inflamed or infected. This is a condition known as folliculitis.
The hair follicles may swell up and fill with pus, and often appear in a cluster.
Heat rash
Heat rash can affect the skin in warm weather. It appears as small, red spots and usually causes an itching or prickling feeling.
Sweating can irritate the rash, so keeping the skin cool can help with symptoms.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Some sexually transmitted infections or STIs can cause spots to form on the scrotum:
- Herpes causes small blisters to appear on the skin.
- Syphilis is now a fairly uncommon STI, but it can cause a sore on the skin.
- Pubic lice, also known as crabs, can cause a rash of small red bumps.
Cysts
Cysts are pus-filled spots that form underneath the skin.
They can appear on any part of the body and are usually harmless unless they become infected.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a virus that affects the skin. It is more common in children and usually does not need treatment.
The main symptom is small, raised spots that are firm to the touch. They form in clusters, usually in creases around the body, such as the armpits and groin.
Close physical contact can spread the virus. To prevent the infection from spreading, a person should not share baths, towels, or clothing.
What does a white, red, or black color mean?
A pimple may appear in a range of colors.
- White pimples usually contain pus.
- Black pimples are often open. Air reaches the oil blocking the pore, causing a reaction that turns it black.
- Redness is usually a sign of irritation or swelling.
An STI or other infection can cause red spots or a rash. Black or white pimples are more likely to be caused by the pores clogged with oil or dead skin cells.
When to see a doctor
If pimples appear on the scrotum repeatedly, people may wish to seek medical advice.
Pimples that appear in clusters, or look like they may be a rash, can be a virus or infection that may need treatment.
If someone has symptoms of an STI, they should see a doctor. Symptoms can include itching, fever, pain when urinating, and discharge from the penis.
What are the treatment options?
Pimples often do not need any treatment. They should disappear on their own within 1 to 2 weeks.
An ingrown hair should be left alone, as it will usually work its way out of the hair follicle naturally.
Folliculitis usually does not need treatment, but a person should see a doctor if it lasts for more than a week.
Using chemicals on the body can irritate pimples. The skin should be kept clean and dry, using warm water and gentle soap for washing.
Do not pick or scratch a pimple, as this can damage it. A pimple that has burst or bled is more likely to become infected.
Heat rash can be treated at home by:
- applying a cool, wet flannel to skin to soothe irritation
- having a cool shower or bath
- wearing loose-fitting clothing
- staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
Pimples that are caused by an infection or virus may need treatment. A doctor will be able to advise on the right course of action.
If a person has an STI, they may need to take a course of antibiotics. Abstaining from sexual contact until the infection has cleared will prevent it being spread to others.
Prevention
Good hygiene can help to prevent pimples. Wearing clean underwear and showering every day can help to stop pimples from developing. Taking a shower after exercise or sweating a lot can help to prevent sweat clogging pores, which can lead to pimples.
Loose-fitting underwear made from natural fabrics can stop heat and moisture from building up. If pimples are caused by ingrown hairs, avoiding shaving can prevent them from developing. Hair removal cream is less likely to cause ingrown hairs than shaving.
Takeaway
Most pimples are harmless, and will usually go away on their own. Anyone with recurrent pimples on the scrotum should consider seeing a doctor or take preventive measures.
People who have symptoms that may indicate an STI should see a doctor for a diagnosis.
SOURCE: MEDICAL NEWS TODAY
Comments
Post a Comment